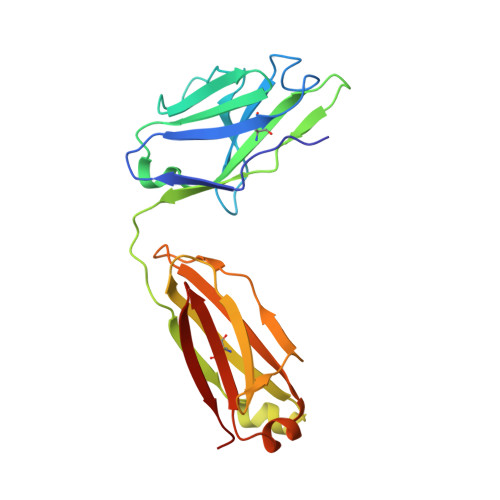
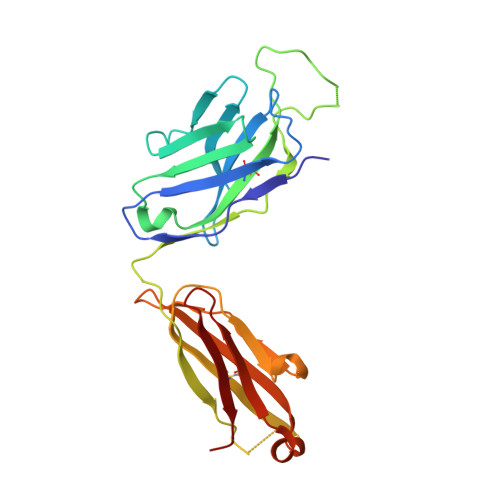
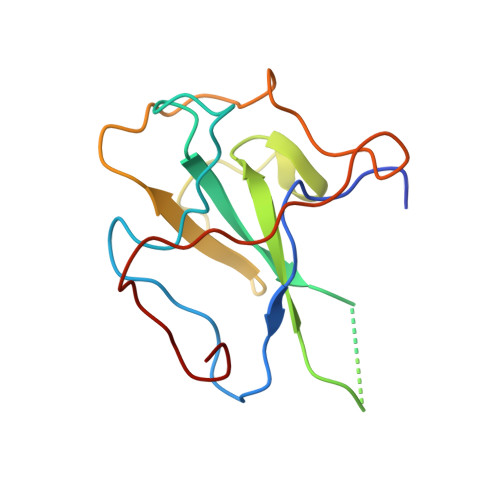
Epitopes recognition of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid RNA binding domain by human monoclonal antibodies.
Kim, Y., Maltseva, N., Tesar, C., Jedrzejczak, R., Endres, M., Ma, H., Dugan, H.L., Stamper, C.T., Chang, C., Li, L., Changrob, S., Zheng, N.Y., Huang, M., Ramanathan, A., Wilson, P., Michalska, K., Joachimiak, A.(2024) iScience 27: 108976-108976
- PubMed: 38327783
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2024.108976
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6VYO, 6WKP, 7N3C, 7N3D, 7STR, 7STS, 7SUE - PubMed Abstract:
Coronavirus nucleocapsid protein (NP) of SARS-CoV-2 plays a central role in many functions important for virus proliferation including packaging and protecting genomic RNA. The protein shares sequence, structure, and architecture with nucleocapsid proteins from betacoronaviruses. The N-terminal domain (NP RBD ) binds RNA and the C-terminal domain is responsible for dimerization. After infection, NP is highly expressed and triggers robust host immune response. The anti-NP antibodies are not protective and not neutralizing but can effectively detect viral proliferation soon after infection. Two structures of SARS-CoV-2 NP RBD were determined providing a continuous model from residue 48 to 173, including RNA binding region and key epitopes. Five structures of NP RBD complexes with human mAbs were isolated using an antigen-bait sorting. Complexes revealed a distinct complement-determining regions and unique sets of epitope recognition. This may assist in the early detection of pathogens and designing peptide-based vaccines. Mutations that significantly increase viral load were mapped on developed, full length NP model, likely impacting interactions with host proteins and viral RNA.
- Center for Structural Biology of Infectious Diseases, Consortium for Advanced Science and Engineering, University of Chicago, Chicago, IL 60367, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: