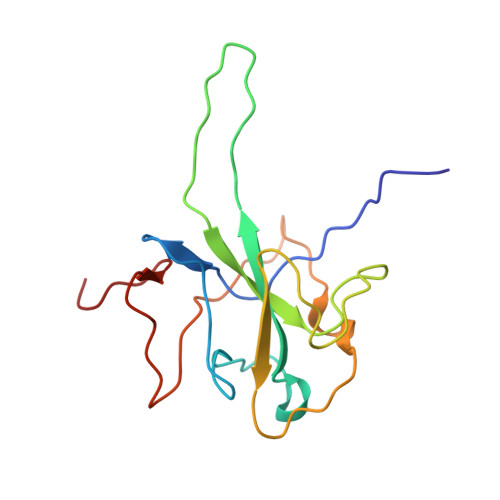
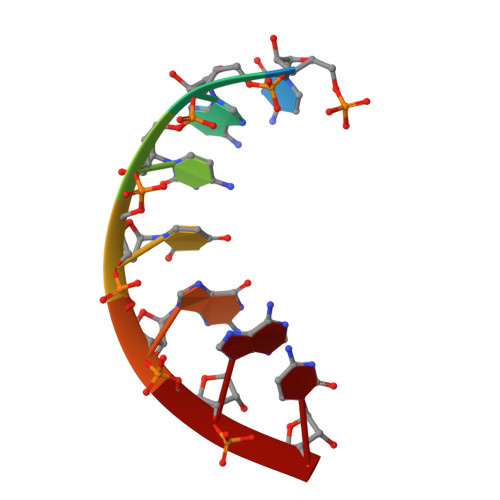
Structural basis of RNA recognition by the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid phosphoprotein.
Dinesh, D.C., Chalupska, D., Silhan, J., Koutna, E., Nencka, R., Veverka, V., Boura, E.(2020) PLoS Pathog 16: e1009100-e1009100
- PubMed: 33264373
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1009100
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6YI3, 7ACS, 7ACT - PubMed Abstract:
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is the causative agent of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). SARS-CoV-2 is a single-stranded positive-sense RNA virus. Like other coronaviruses, SARS-CoV-2 has an unusually large genome that encodes four structural proteins and sixteen nonstructural proteins. The structural nucleocapsid phosphoprotein N is essential for linking the viral genome to the viral membrane. Both N-terminal RNA binding (N-NTD) and C-terminal dimerization domains are involved in capturing the RNA genome and, the intrinsically disordered region between these domains anchors the ribonucleoprotein complex to the viral membrane. Here, we characterized the structure of the N-NTD and its interaction with RNA using NMR spectroscopy. We observed a positively charged canyon on the surface of the N-NTD that might serve as a putative RNA binding site similarly to other coronaviruses. The subsequent NMR titrations using single-stranded and double-stranded RNA revealed a much more extensive U-shaped RNA-binding cleft lined with regularly distributed arginines and lysines. The NMR data supported by mutational analysis allowed us to construct hybrid atomic models of the N-NTD/RNA complex that provided detailed insight into RNA recognition.
- Institute of Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry of the Czech Academy of Sciences, Prague, Czech Republic.
Organizational Affiliation: