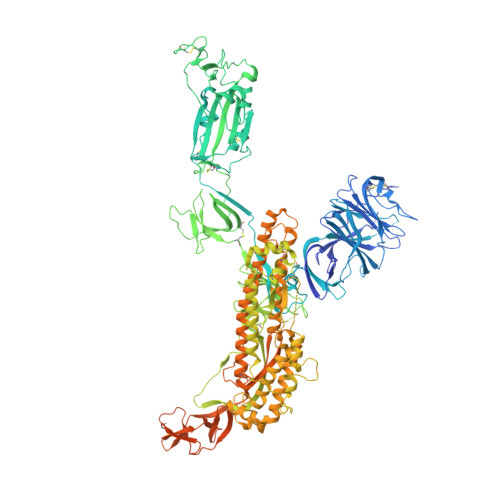
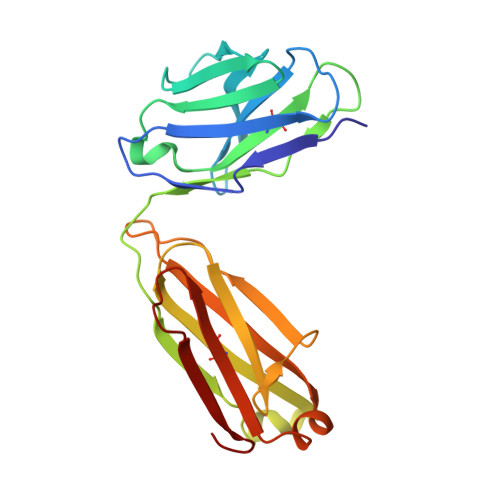
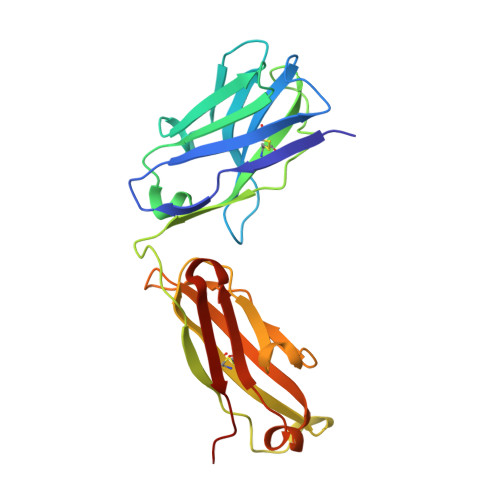
Tetravalent SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies Show Enhanced Potency and Resistance to Escape Mutations.
Miersch, S., Li, Z., Saberianfar, R., Ustav, M., Brett Case, J., Blazer, L., Chen, C., Ye, W., Pavlenco, A., Gorelik, M., Garcia Perez, J., Subramania, S., Singh, S., Ploder, L., Ganaie, S., Chen, R.E., Leung, D.W., Pandolfi, P.P., Novelli, G., Matusali, G., Colavita, F., Capobianchi, M.R., Jain, S., Gupta, J.B., Amarasinghe, G.K., Diamond, M.S., Rini, J., Sidhu, S.S.(2021) J Mol Biology 433: 167177-167177
- PubMed: 34329642
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2021.167177
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7KLG, 7KLH, 7KMK, 7KML, 7KXJ, 7KXK - PubMed Abstract:
Neutralizing antibodies (nAbs) hold promise as therapeutics against COVID-19. Here, we describe protein engineering and modular design principles that have led to the development of synthetic bivalent and tetravalent nAbs against SARS-CoV-2. The best nAb targets the host receptor binding site of the viral S-protein and tetravalent versions block entry with a potency exceeding bivalent nAbs by an order of magnitude. Structural studies show that both the bivalent and tetravalent nAbs can make multivalent interactions with a single S-protein trimer, consistent with the avidity and potency of these molecules. Significantly, we show that the tetravalent nAbs show increased tolerance to potential virus escape mutants and an emerging variant of concern. Bivalent and tetravalent nAbs can be produced at large-scale and are as stable and specific as approved antibody drugs. Our results provide a general framework for enhancing antiviral therapies against COVID-19 and related viral threats, and our strategy can be applied to virtually any antibody drug.
- The Donnelly Centre, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada.
Organizational Affiliation: