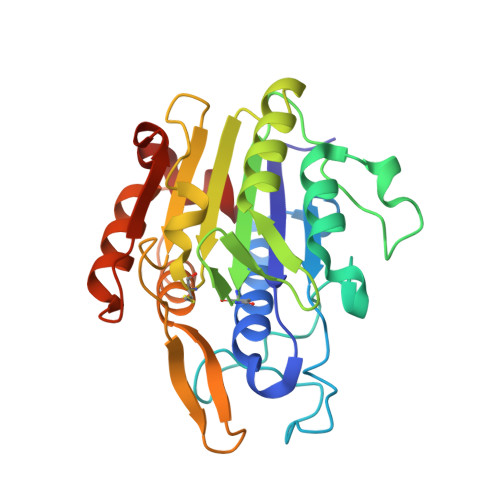
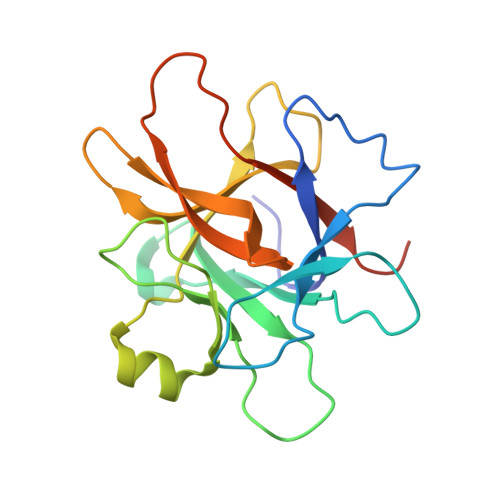
Structural and functional studies of legumain-mycocypin complexes revealed a competitive, exosite-regulated mode of interaction.
Elamin, T., Santos, N.P., Briza, P., Brandstetter, H., Dall, E.(2022) J Biological Chem 298: 102502-102502
- PubMed: 36116553
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102502
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8AE4, 8AE5 - PubMed Abstract:
Under pathophysiologic conditions such as Alzheimer's disease and cancer, the endolysosomal cysteine protease legumain was found to translocate to the cytosol, the nucleus, and the extracellular space. These noncanonical localizations demand for a tight regulation of legumain activity, which is in part conferred by protein inhibitors. While there is a significant body of knowledge on the interaction of human legumain with endogenous cystatins, only little is known on its regulation by fungal mycocypins. Mycocypins are characterized by (i) versatile, plastic surface loops allowing them to inhibit different classes of enzymes and (ii) a high resistance toward extremes of pH and temperature. These properties make mycocypins attractive starting points for biotechnological and medical applications. In this study, we show that mycocypins utilize an adaptable reactive center loop to target the active site of legumain in a substrate-like manner. The interaction was further stabilized by variable, isoform-specific exosites, converting the substrate recognition into inhibition. Additionally, we found that selected mycocypins were capable of covalent complex formation with legumain by forming a disulfide bond to the active site cysteine. Furthermore, our inhibition studies with other clan CD proteases suggested that mycocypins may serve as broad-spectrum inhibitors of clan CD proteases. Our studies uncovered the potential of mycocypins as a new scaffold for drug development, providing the basis for the design of specific legumain inhibitors.
- Department of Biosciences and Medical Biology, University of Salzburg, Salzburg, Austria.
Organizational Affiliation: