Macrocyclic Peptide Probes for Immunomodulatory Protein CD59: Potent Modulators of Bacterial Toxin Activity and Antibody-Dependent Cytotoxicity.
Bickel, J.K., Ahmed, A.I.S., Pidd, A.B., Morgan, R.M., McAllister, T.E., Horrell, S., Couves, E.C., Nagaraj, H., Bartlett, E.J., El Omari, K., Kawamura, A., Bubeck, D., Tate, E.W.(2025) Angew Chem Int Ed Engl : e202422673-e202422673
- PubMed: 40272315
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202422673
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8CN6 - PubMed Abstract:
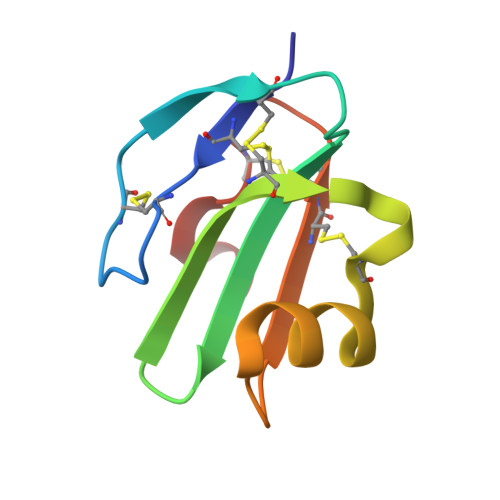
CD59 is an immunomodulatory cell surface receptor associated with human disease. Despite its importance in complement regulation and bacterial pathogenesis, CD59 remains a challenging therapeutic target. Research to date has focused on antibody or protein-based strategies. Here we present a new approach to target CD59 using macrocyclic peptides with low nanomolar affinity for CD59. Through X-ray crystallographic studies and structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies, we identify key interactions that are essential for binding and activity. We find that the macrocyclic peptide CP-06 adopts a beta-hairpin structure and binds CD59 through an intermolecular beta-sheet, mimicking protein-protein interactions of biologically relevant CD59 interaction partners. We create dimeric and lipidated macrocyclic peptide conjugates as enhanced cell-active CD59 inhibitors and show that these probes can be used to modulate both complement-mediated killing of human cells and lytic activity of bacterial virulence factors. Together, our data provide a starting point for future development of macrocyclic peptides to target CD59 activity in diverse cellular contexts.
- Department of Chemistry, Molecular Sciences Research Hub, Imperial College London, London, W12 0BZ, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: