Development of Orally Bioavailable Peptides Targeting an Intracellular Protein: From a Hit to a Clinical KRAS Inhibitor.
Tanada, M., Tamiya, M., Matsuo, A., Chiyoda, A., Takano, K., Ito, T., Irie, M., Kotake, T., Takeyama, R., Kawada, H., Hayashi, R., Ishikawa, S., Nomura, K., Furuichi, N., Morita, Y., Kage, M., Hashimoto, S., Nii, K., Sase, H., Ohara, K., Ohta, A., Kuramoto, S., Nishimura, Y., Iikura, H., Shiraishi, T.(2023) J Am Chem Soc 145: 16610-16620
- PubMed: 37463267
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.3c03886
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
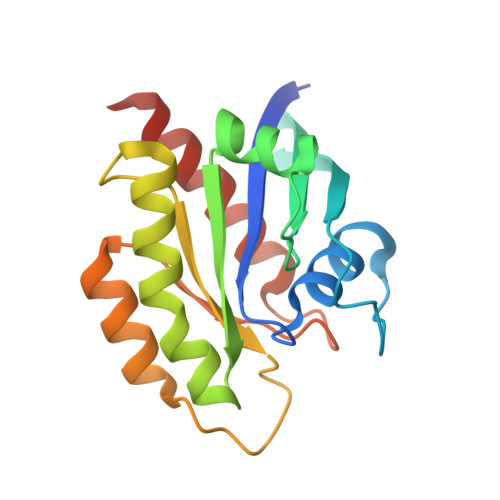
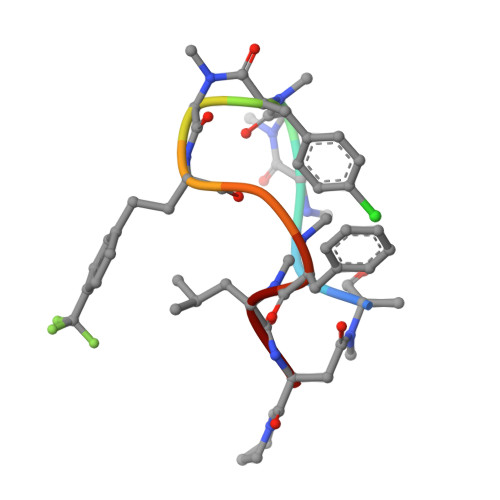
8JJS - PubMed Abstract:
Cyclic peptides as a therapeutic modality are attracting a lot of attention due to their potential for oral absorption and accessibility to intracellular tough targets. Here, starting with a drug-like hit discovered using an mRNA display library, we describe a chemical optimization that led to the orally available clinical compound known as LUNA18, an 11-mer cyclic peptide inhibitor for the intracellular tough target RAS. The key findings are as follows: (i) two peptide side chains were identified that each increase RAS affinity over 10-fold; (ii) physico-chemical properties (PCP) including C log P can be adjusted by side-chain modification to increase membrane permeability; (iii) restriction of cyclic peptide conformation works effectively to adjust PCP and improve bio-activity; (iv) cellular efficacy was observed in peptides with a permeability of around 0.4 × 10 -6 cm/s or more in a Caco-2 permeability assay; and (v) while keeping the cyclic peptide's main-chain conformation, we found one example where the RAS protein structure was changed dramatically through induced-fit to our peptide side chain. This study demonstrates how the chemical optimization of bio-active peptides can be achieved without scaffold hopping, much like the processes for small molecule drug discovery that are guided by Lipinski's rule of five. Our approach provides a versatile new strategy for generating peptide drugs starting from drug-like hits.
Organizational Affiliation:
Research Division, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., 216, Totsuka-cho, Totsuka-ku, Yokohama, Kanagawa 244-8602, Japan.