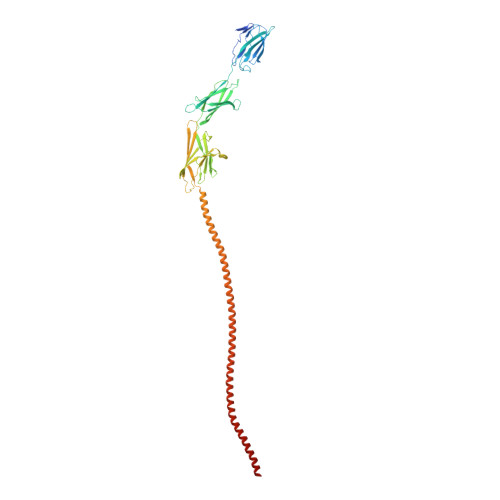
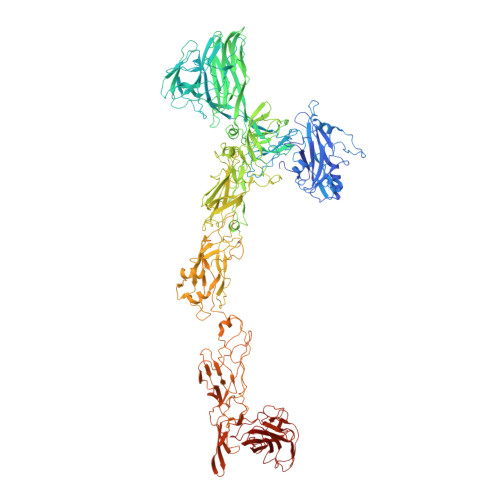
Structure of the two-component S-layer of the archaeon Sulfolobus acidocaldarius.
Gambelli, L., McLaren, M., Conners, R., Sanders, K., Gaines, M.C., Clark, L., Gold, V.A.M., Kattnig, D., Sikora, M., Hanus, C., Isupov, M.N., Daum, B.(2024) Elife 13
- PubMed: 38251732
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.84617
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7ZCX, 8AN2, 8AN3, 8QOX, 8QP0 - PubMed Abstract:
Surface layers (S-layers) are resilient two-dimensional protein lattices that encapsulate many bacteria and most archaea. In archaea, S-layers usually form the only structural component of the cell wall and thus act as the final frontier between the cell and its environment. Therefore, S-layers are crucial for supporting microbial life. Notwithstanding their importance, little is known about archaeal S-layers at the atomic level. Here, we combined single-particle cryo electron microscopy, cryo electron tomography, and Alphafold2 predictions to generate an atomic model of the two-component S-layer of Sulfolobus acidocaldarius . The outer component of this S-layer (SlaA) is a flexible, highly glycosylated, and stable protein. Together with the inner and membrane-bound component (SlaB), they assemble into a porous and interwoven lattice. We hypothesise that jackknife-like conformational changes in SlaA play important roles in S-layer assembly.
- Living Systems Institute, University of Exeter, Exeter, United Kingdom.
Organizational Affiliation: