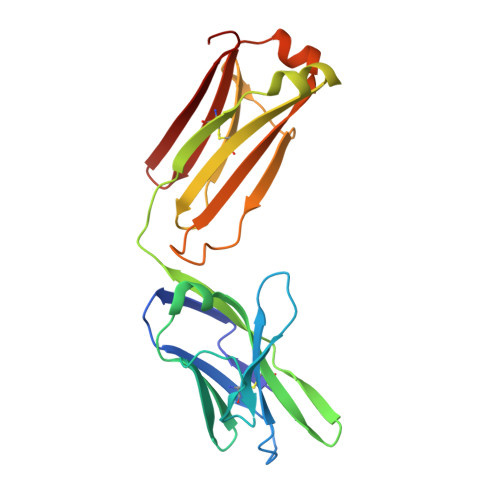
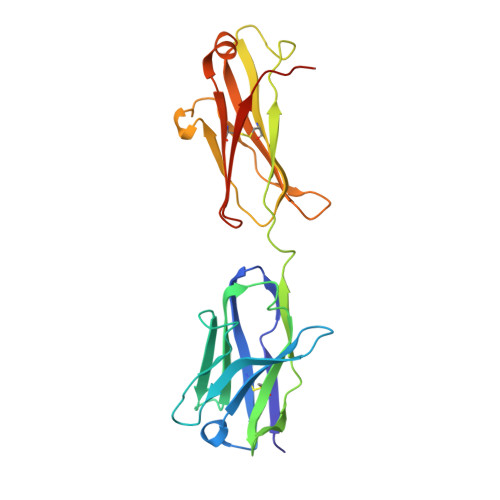
Antigen-binding fragments with improved crystal lattice packing and enhanced conformational flexibility at the elbow region as crystallization chaperones.
Bruce, H.A., Singer, A.U., Blazer, L.L., Luu, K., Ploder, L., Pavlenco, A., Kurinov, I., Adams, J.J., Sidhu, S.S.(2024) Protein Sci 33: e5081-e5081
- PubMed: 38924648
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.5081
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8VTP, 8VTR, 8VU1, 8VU4, 8VUA, 8VUC, 8VUI, 8VVM, 8VVO - PubMed Abstract:
It has been shown previously that a set of three modifications-termed S1, Crystal Kappa, and elbow-act synergistically to improve the crystallizability of an antigen-binding fragment (Fab) framework. Here, we prepared a phage-displayed library and performed crystallization screenings to identify additional substitutions-located near the heavy-chain elbow region-which cooperate with the S1, Crystal Kappa, and elbow modifications to increase expression and improve crystallizability of the Fab framework even further. One substitution (K141Q) supports the signature Crystal Kappa-mediated Fab:Fab crystal lattice packing interaction. Another substitution (E172G) improves the compatibility of the elbow modification with the Fab framework by alleviating some of the strain incurred by the shortened and bulkier elbow linker region. A third substitution (F170W) generates a split-Fab conformation, resulting in a powerful crystal lattice packing interaction comprising the biological interaction interface between the variable heavy and light chain domains. In sum, we have used K141Q, E172G, and F170W substitutions-which complement the S1, Crystal Kappa, and elbow modifications-to generate a set of highly crystallizable Fab frameworks that can be used as chaperones to enable facile elucidation of Fab:antigen complex structures by x-ray crystallography.
- School of Pharmacy, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario, Canada.
Organizational Affiliation: