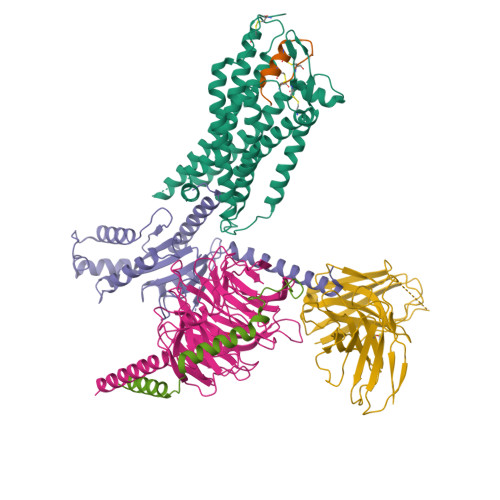
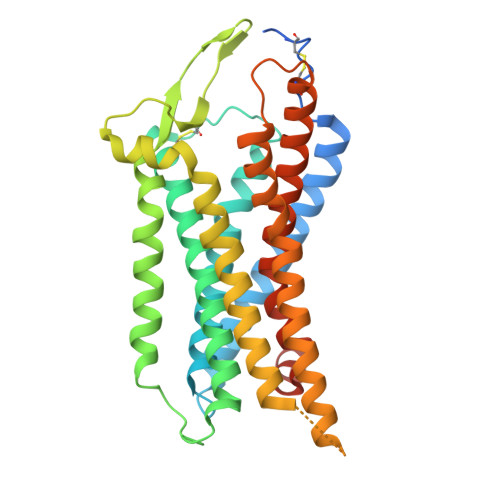
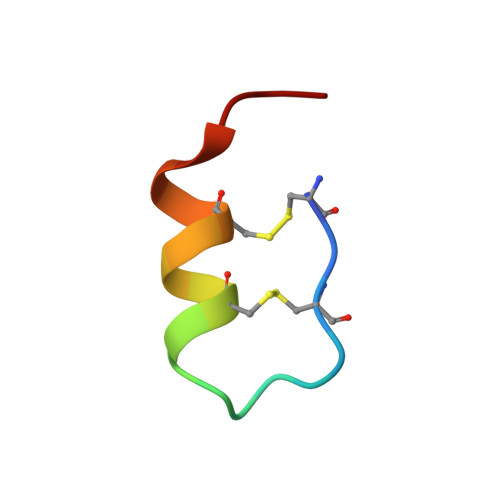
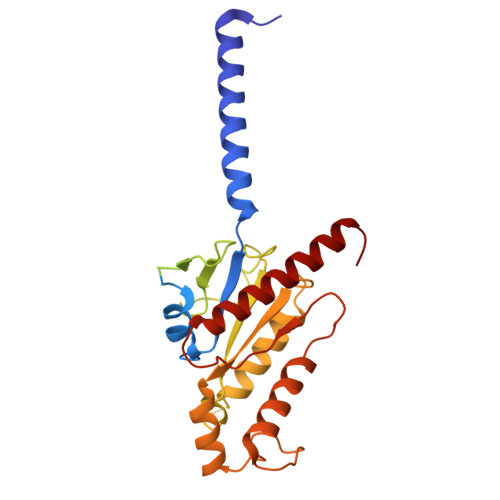
Structure of endothelin ET B receptor-G i complex in a conformation stabilized by unique NPxxL motif.
Tani, K., Maki-Yonekura, S., Kanno, R., Negami, T., Hamaguchi, T., Hall, M., Mizoguchi, A., Humbel, B.M., Terada, T., Yonekura, K., Doi, T.(2024) Commun Biol 7: 1303-1303
- PubMed: 39414992
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-024-06905-z
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8XWP, 8XWQ, 8ZRT - PubMed Abstract:
Endothelin type B receptor (ET B R) plays a crucial role in regulating blood pressure and humoral homeostasis, making it an important therapeutic target for related diseases. ET B R activation by the endogenous peptide hormones endothelin (ET)-1-3 stimulates several signaling pathways, including G s , G i/o , G q/11 , G 12/13 , and β-arrestin. Although the conserved NPxxY motif in transmembrane helix 7 (TM7) is important during GPCR activation, ET B R possesses the lesser known NPxxL motif. In this study, we present the cryo-EM structure of the ET B R-G i complex, complemented by MD simulations and functional studies. These investigations reveal an unusual movement of TM7 to the intracellular side during ET B R activation and the essential roles of the diverse NPxxL motif in stabilizing the active conformation of ET B R and organizing the assembly of the binding pocket for the α5 helix of G i protein. These findings enhance our understanding of the interactions between GPCRs and G proteins, thereby advancing the development of therapeutic strategies.
Organizational Affiliation:
Center for Computational Sciences, University of Tsukuba, 1-1-1 Tennodai, Tsukuba, Ibaraki, 305-8577, Japan. ktani@ccs.tsukuba.ac.jp.