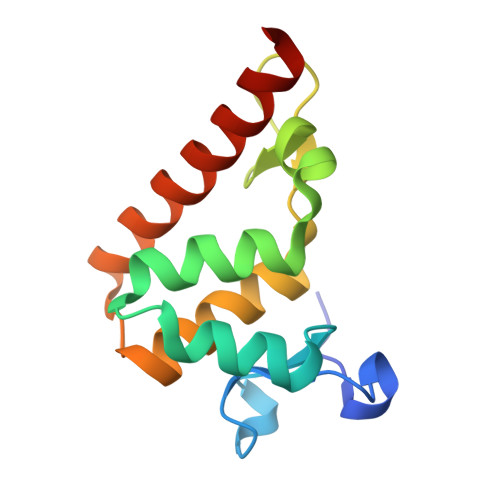
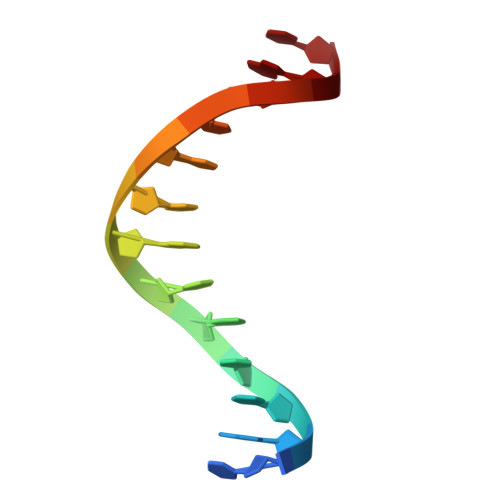
Structural basis of DNA recognition by BEN domain proteins reveals a role for oligomerization in unmethylated DNA selection by BANP.
Ren, J., Wang, J., Ren, Y., Zhang, Y., Wei, P., Wang, M., Zhang, Y., Li, M., Yuan, C., Gong, H., Jiang, J., Wang, Z.(2024) Nucleic Acids Res 52: 11349-11361
- PubMed: 39225042
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkae762
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8YZS, 8YZT - PubMed Abstract:
The BEN domain is a newly discovered type of DNA-binding domain that exists in a variety of species. There are nine BEN domain-containing proteins in humans, and most have been shown to have chromatin-related functions. NACC1 preferentially binds to CATG motif-containing sequences and functions primarily as a transcriptional coregulator. BANP and BEND3 preferentially bind DNA bearing unmethylated CpG motifs, and they function as CpG island-binding proteins. To date, the DNA recognition mechanism of quite a few of these proteins remains to be determined. In this study, we solved the crystal structures of the BEN domains of NACC1 and BANP in complex with their cognate DNA substrates. We revealed the details of DNA binding by these BEN domain proteins and unexpectedly revealed that oligomerization is required for BANP to select unmethylated CGCG motif-containing DNA substrates. Our study clarifies the controversies surrounding DNA recognition by BANP and demonstrates a new mechanism by which BANP selects unmethylated CpG motifs and functions as a CpG island-binding protein. This understanding will facilitate further exploration of the physiological functions of the BEN domain proteins in the future.
- Key Laboratory of Cell Proliferation and Regulation Biology of Ministry of Education, College of Life Sciences, Beijing Normal University, 19 Xinjiekouwai Avenue, Beijing 100875, China.
Organizational Affiliation: