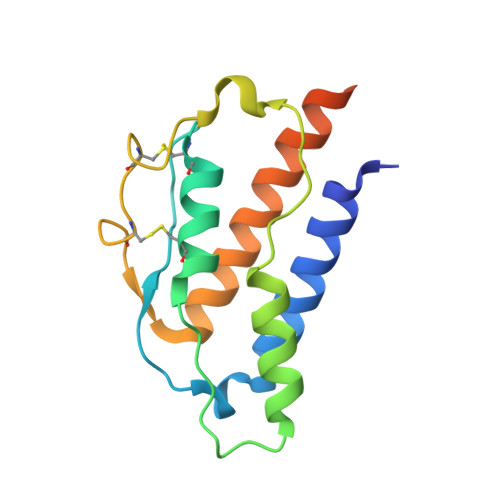
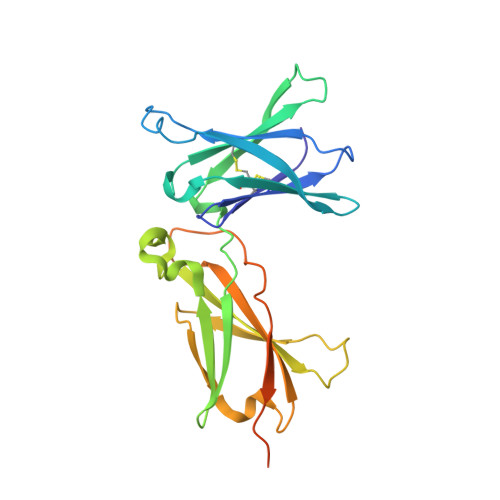
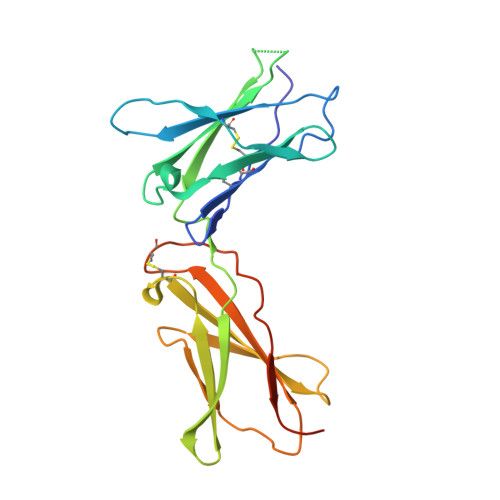
A structural blueprint for interleukin-21 signal modulation.
Abhiraman, G.C., Bruun, T.U.J., Caveney, N.A., Su, L.L., Saxton, R.A., Yin, Q., Tang, S., Davis, M.M., Jude, K.M., Garcia, K.C.(2023) Cell Rep 42: 112657-112657
- PubMed: 37339051
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112657
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8ENT - PubMed Abstract:
Interleukin-21 (IL-21) plays a critical role in generating immunological memory by promoting the germinal center reaction, yet clinical use of IL-21 remains challenging because of its pleiotropy and association with autoimmune disease. To better understand the structural basis of IL-21 signaling, we determine the structure of the IL-21-IL-21R-γc ternary signaling complex by X-ray crystallography and a structure of a dimer of trimeric complexes using cryo-electron microscopy. Guided by the structure, we design analogs of IL-21 by introducing substitutions to the IL-21-γc interface. These IL-21 analogs act as partial agonists that modulate downstream activation of pS6, pSTAT3, and pSTAT1. These analogs exhibit differential activity on T and B cell subsets and modulate antibody production in human tonsil organoids. These results clarify the structural basis of IL-21 signaling and offer a potential strategy for tunable manipulation of humoral immunity.
- Department of Molecular and Cellular Physiology, Stanford University School of Medicine, 279 Campus Drive, Stanford, CA 94305, USA; Program in Immunology, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, CA 94305, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: