Donor strand complementation and calcium ion coordination drive the chaperone-free polymerization of archaeal cannulae.
Sleutel, M., Sonani, R.R., Miller, J.G., Wang, F., Gonzalez Socorro, A., Chen, Y., Martin, R., Demeler, B., Rudolph, M.J., Alva, V., Remaut, H., Egelman, E.H., Conticello, V.P.(2025) Nat Commun 16: 9082-9082
- PubMed: 41083437
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-64120-8
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9BAB, 9BAC - PubMed Abstract:
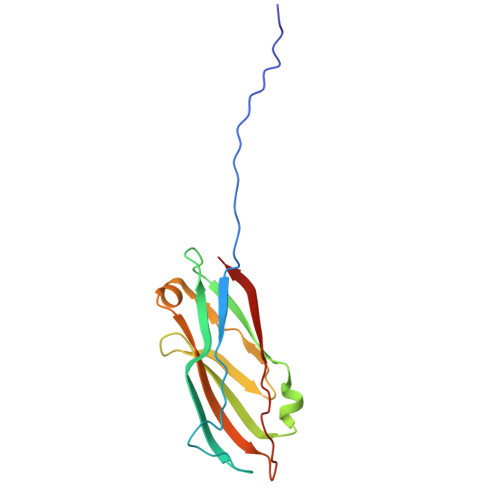
Cannulae are structurally rigid tubular protein filaments that accumulate on the extracellular surface of archaea within the family Pyrodictiaceae during cell growth. These obligate anaerobes propagate under hyperthermophilic conditions in which cannulae form a biomatrix that interconnects and sustains cells. The persistence of cannulae in this environment suggests that these filaments display significant thermostability, which has attracted technological interest in their development as synthetic protein-based biomaterials. Here, we report cryoEM structural analyses of ex vivo and in vitro assembled recombinant cannulae. We demonstrate that the interactions between protomers in native and recombinant cannulae is based on donor strand complementation (DSC), a form of non-covalent polymerization previously observed for bacterial chaperone-usher pili. Unexpectedly, calcium ion coordination at the subunit interfaces reinforces the network of donor strand interactions in the cannulae. This study provides insight into the mechanism of assembly of cannulae and the structural origin of their high stability and rigidity.
- Structural Biology Brussels, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Brussels, Belgium.
Organizational Affiliation: