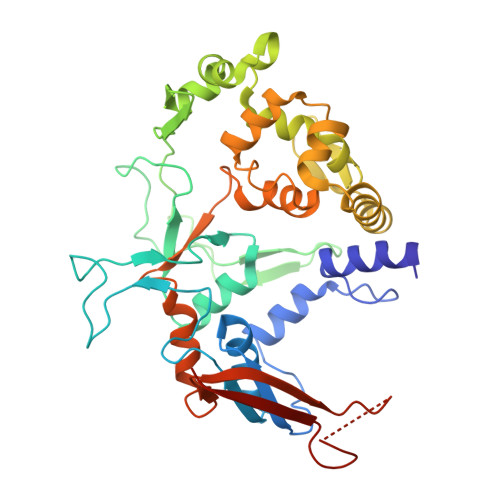
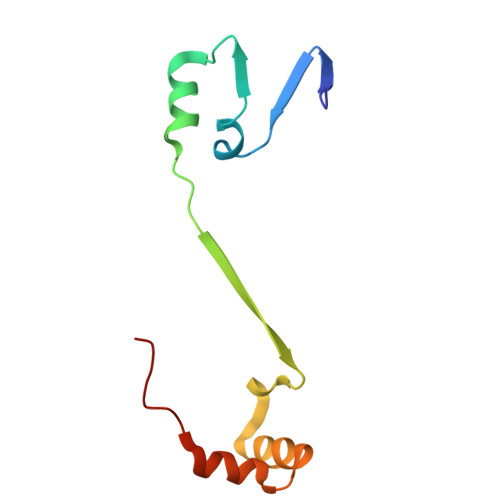
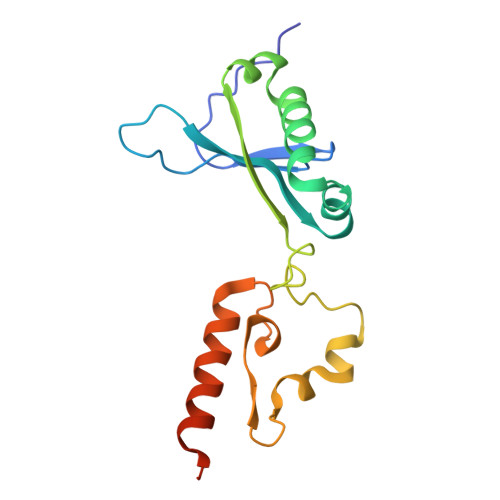
Substrate recognition mechanisms of ʟ-glutamate oxidase from Streptomyces sp. and its conversion to ʟ-tyrosine oxidase.
Ueda, Y., Yano, Y., Nakayama, N., Takekawa, N., Inagaki, K., Imada, K.(2026) Protein Sci 35: e70432-e70432
- PubMed: 41432352
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.70432
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9W54, 9W55, 9W56, 9W57, 9W58 - PubMed Abstract:
ʟ-Amino acid oxidase (LAAO) is a flavoenzyme that catalyzes the oxidative deamination of ʟ-amino acids, producing α-keto acids, ammonia, and hydrogen peroxide. Among LAAOs, ʟ-glutamate oxidase (LGOX) from Streptomyces sp. X-119-6 exhibits exceptionally high substrate specificity for ʟ-glutamate. LGOX is expressed as a homodimeric precursor and undergoes proteolytic processing for maturation. Structural studies revealed that LGOX comprises an FAD-binding domain, a substrate-binding domain, and a helical domain. Conserved residues W653, R124, and Y562 that recognize the α-amino and α-carboxyl groups of the substrate exist in the putative active site. R305 was identified as a key determinant for side-chain recognition; its substitution with Glu conferred specific activity toward ʟ-arginine, effectively converting LGOX into an ʟ-arginine oxidase. However, the putative substrate binding pocket includes an acidic residue, E617, undesirable for acidic substrates. Therefore, the mechanism of high specificity for ʟ-glutamate remains unclear. To elucidate the molecular basis for the high substrate specificity of LGOX, we determined the structure of LGOX in complex with ʟ-glutamate. Structural and mutational analyses revealed that E617 plays a critical role in substrate binding by aligning the side chain of R305. The loop at the entrance of the tunnel to the substrate-binding site regulates the access of the substrate to the site. Furthermore, E617F and E617K variants acquired ʟ-tyrosine oxidase activity, providing insight into how specificity can be redirected. These findings clarify the substrate recognition mechanism of LGOX and underscore its potential as a robust scaffold for engineering novel amino acid oxidases with tailored specificities.
- Department of Macromolecular Science, Graduate School of Science, The University of Osaka, Toyonaka, Osaka, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: