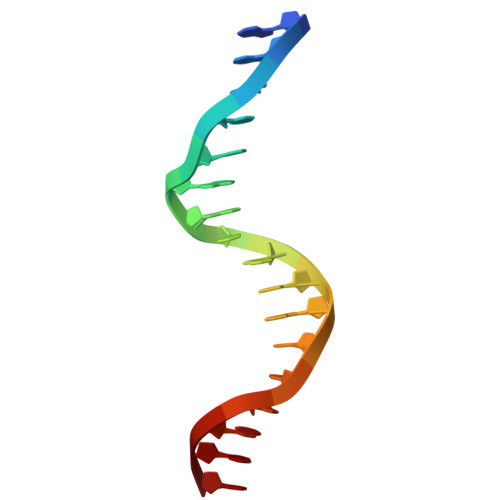
Biochemical and structural studies of NFIA and NFIC reveal a conserved mechanism for specific DNA recognition and provide insight into potential pathogenicity of disease-associated mutations.
Pan, S., Pei, W., Zhang, J., Min, J., Liu, K.(2025) Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai)
- PubMed: 41408833
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3724/abbs.2025236
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9XVD, 9XVF, 9XVO, 9XVQ - PubMed Abstract:
Nuclear factor I (NFI) transcription factors play essential roles in multiple aspects of nervous system development, including radial glia maturation, neurogenesis, gliogenesis, and brain morphogenesis. Numerous NFI variants have been identified in individuals with neurodevelopmental disorders, yet the molecular basis of their pathogenicity remains unclear. The absence of resolved NFI-DNA complex structures continues to impede mechanistic insights and therapeutic exploration. Here, we define the oligomeric states of NFIA and NFIC, and determine the crystal structures of the NFIC homodimer, as well as the NFIA and NFIC monomers lacking their dimerization region, in complexes with double-stranded DNAs. Structural analysis reveals the molecular mechanism underlying NFI dimerization and recognition of a dyad-symmetric TGGCA(N3)TGCCA sequence motif, and demonstrates that dimerization enhances both DNA-binding affinity and specificity of NFI proteins. The functional importance of key NFI residues and DNA bases involved in the protein-DNA interaction is further validated by mutagenesis and binding assays. Additionally, we systematically evaluate the effects of the neurodevelopmental disorders-associated NFI mutations on DNA binding of NFIA, providing insights into their potential pathogenic mechanisms. Together, our findings elucidate the structural basis of NFI dimerization and dyad-symmetric DNA recognition and highlight pathogenic variants for further mechanistic studies in neurodevelopmental disorders.