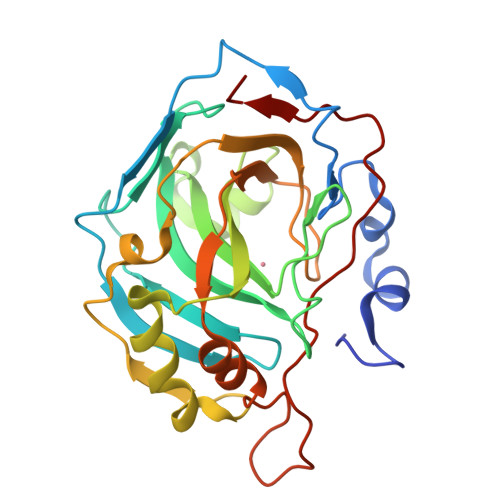
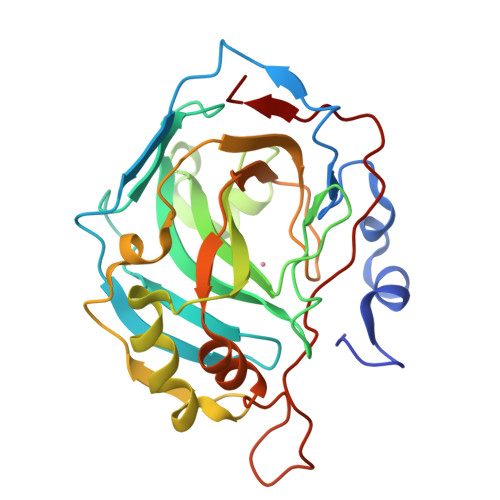
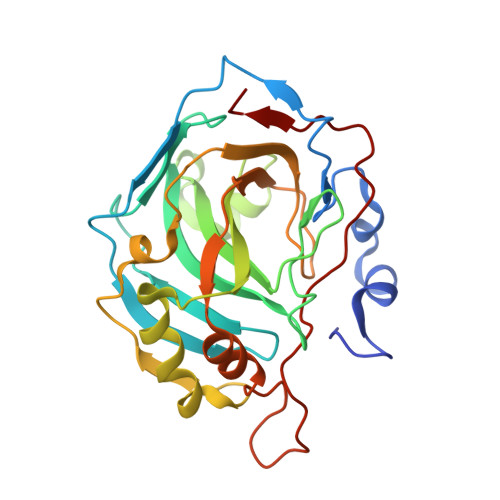
Comparison of solution and crystal properties of Co(II)-substituted human carbonic anhydrase II.
Avvaru, B.S., Arenas, D.J., Tu, C., Tanner, D.B., McKenna, R., Silverman, D.N.(2010) Arch Biochem Biophys 502: 53-59
- PubMed: 20637176
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2010.07.010
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3KOI, 3KOK, 3KON - PubMed Abstract:
The visible absorption of crystals of Co(II)-substituted human carbonic anhydrase II (Co(II)-HCA II) were measured over a pH range of 6.0-11.0 giving an estimate of pK(a) 8.4 for the ionization of the metal-bound water in the crystal. This is higher by about 1.2 pK(a) units than the pK(a) near 7.2 for Co(II)-CA II in solution. This effect is attributed to a nonspecific ionic strength effect of 1.4M citrate in the precipitant solution used in the crystal growth. A pK(a) of 8.3 for the aqueous ligand of the cobalt was measured for Co(II)-HCA II in solution containing 0.8M citrate. Citrate is not an inhibitor of the catalytic activity of Co(II)-HCA II and was not observed in crystal structures. The X-ray structures at 1.5-1.6A resolution of Co(II)-HCA II were determined for crystals prepared at pH 6.0, 8.5 and 11.0 and revealed no conformational changes of amino-acid side chains as a result of the use of citrate. However, the studies of Co(II)-HCA II did reveal a change in metal coordination from tetrahedral at pH 11 to a coordination consistent with a mixed population of both tetrahedral and penta-coordinate at pH 8.5 to an octahedral geometry characteristic of the oxidized enzyme Co(III)-HCA II at pH 6.0.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL 32610, USA.