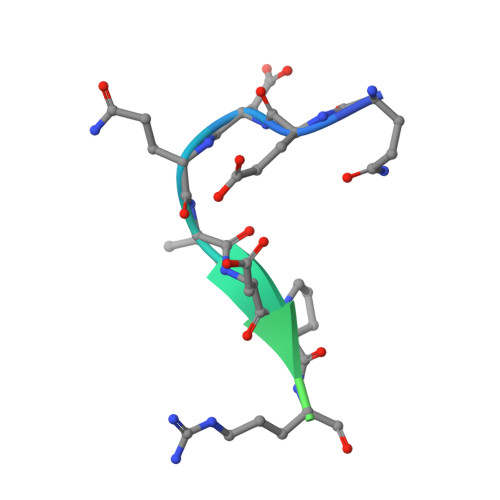
Exposure of R169 controls protein C activation and autoactivation.
Pozzi, N., Barranco-Medina, S., Chen, Z., Di Cera, E.(2012) Blood 120: 664-670
- PubMed: 22535660
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2012-03-415323
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4DT7 - PubMed Abstract:
Protein C is activated by thrombin with a value of k(cat)/K(m) = 0.11mM(-1)s(-1) that increases 1700-fold in the presence of the cofactor thrombomodulin. The molecular origin of this effect triggering an important feedback loop in the coagulation cascade remains elusive. Acidic residues in the activation domain of protein C are thought to electrostatically clash with the active site of thrombin. However, functional and structural data reported here support an alternative scenario. The thrombin precursor prethrombin-2 has R15 at the site of activation in ionic interaction with E14e, D14l, and E18, instead of being exposed to solvent for proteolytic attack. Residues E160, D167, and D172 around the site of activation at R169 of protein C occupy the same positions as E14e, D14l, and E18 in prethrombin-2. Caging of R169 by E160, D167, and D172 is responsible for much of the poor activity of thrombin toward protein C. The E160A/D167A/D172A mutant is activated by thrombin 63-fold faster than wild-type in the absence of thrombomodulin and, over a slower time scale, spontaneously converts to activated protein C. These findings establish a new paradigm for cofactor-assisted reactions in the coagulation cascade.
- Edward A Doisy Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, St Louis University School of Medicine, St Louis, MO 63110, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: